Approaches To Estimating the Waterborne Disease Outbreak Burden In the U.S.: Uses and Limitations of the Waterborne Disease Outbreak Surveillance System (External Review Draft)
Alert
Notice - This site contains archived material(s)
Archive disclaimer
Archived files are provided for reference purposes only.
The file was current when produced, but is no longer maintained and may now be outdated.
Persons with disabilities having difficulty accessing archived files may contact the Risk Webmaster for assistance.
Please use the contact us form if you need additional support.
Abstract
The Approaches to Estimating the Waterborne Disease Outbreak Burden in the United States: Uses and Limitations of the Waterborne Disease Outbreak Surveillance System (External Review Draft) document presents approaches for estimating the epidemiologic and economic burden of disease associated with 665 WBDOs reported in the U.S. between 1971 and 2000. The term disease burden broadly refers to the magnitude of the impact incurred by society as a consequence of disease in the community (e.g. decrements in a population's health or the associated economic effects) and there are various metrics that can be employed by analysts to quantify burden. The external review draft report also includes recommendations for the collection and reporting of additional outbreak information that would improve the usefulness of the WBDO database for future disease burden estimates.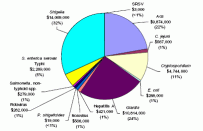 Information about U.S. Waterborne Disease Outbreaks (WBDOs) is voluntarily reported by state, territorial and local public health agencies to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). CDC and EPA jointly maintain the WBDO database that summarizes the information collected through this WBDO Surveillance System. The WBDO database describes outbreak attributes including, among other things, the drinking water system deficiency, the etiologic agent, and the number of individuals who became ill. Underreporting of WBDOs is assumed but the magnitude of underreporting is unknown.
Information about U.S. Waterborne Disease Outbreaks (WBDOs) is voluntarily reported by state, territorial and local public health agencies to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). CDC and EPA jointly maintain the WBDO database that summarizes the information collected through this WBDO Surveillance System. The WBDO database describes outbreak attributes including, among other things, the drinking water system deficiency, the etiologic agent, and the number of individuals who became ill. Underreporting of WBDOs is assumed but the magnitude of underreporting is unknown.
Impact/Purpose
Information about U.S. Waterborne Disease Outbreaks (WBDOs) is voluntarily reported by state, territorial and local public health agencies to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). CDC and EPA jointly maintain the WBDO database that summarizes the information collected through this WBDO Surveillance System. The WBDO database describes outbreak attributes including, among other things, the drinking water system deficiency, the etiologic agent, and the number of individuals who became ill. Underreporting of WBDOs is assumed but the magnitude of underreporting is unknown.Status
Following the external peer review and public comment period, EPA will incorporate the comments in a Final report to be release in 2007 on the NCEA website.Citation
U. S. EPA. Approaches To Estimating the Waterborne Disease Outbreak Burden In the U.S.: Uses and Limitations of the Waterborne Disease Outbreak Surveillance System (External Review Draft). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D.C., EPA/600/R-06/066, 2006.History/Chronology
| Date | Description |
|---|---|
| 01- Sep 2006 | EPA released the External Review Draft Document for a 30-day Public Comment Period. |
| 02- Oct 2006 | EPA held an External Peer Review Meeting on the draft document in late October. Following the external peer review and public comment period, EPA will incorporate these comments into the final report. |
Additional Information
Information collected on WBDOs is published biennially in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Reports. For example:- Oct 22, 2004 surveillance summary for 2001/2002 (PDF, 48pp)
- Nov 22, 2002 surveillance summary for 1999/2000 (PDF, 52pp)
- May 26, 2000 surveillance summary for 1997/1998 (PDF, 44pp)
Download(s)
This download(s) is distributed solely for the purpose of pre-dissemination peer review under applicable information quality guidelines. It has not been formally disseminated by EPA. It does not represent and should not be construed to represent any Agency determination or policy.
